讨论班 | 时空统计、统计基础、网络分析(2021/12/13-2021/12/19)
1、讨论班简介
时空统计讨论班
本讨论班目前以讲述《Statistics for Spatio-Temporal Data》(Noel Cressie, 2011)为主,辅以经典的时空统计论文阅读。主要内容为时空统计所需要的空间统计、时间序列分析基础,以及在基础之上建立的分层动态时空模型(Hierarchical DSTMs)。
统计基础讨论班
本讨论班目前主要参考书籍为《Statistical Models》(A. C. Davison,2008),开展目的是为新生补充研究生阶段所需的统计方面的基本知识。
网络分析讨论班
图结构的数据在自然科学和社会科学中都是普遍存在的,这门课程我们将基于《Graph Representation Learning》讨论图的理论以及网络分析的理论,介绍节点嵌入的方法。此外,我们还将介绍图神经网络的应用与理论、图的深度生成模型。
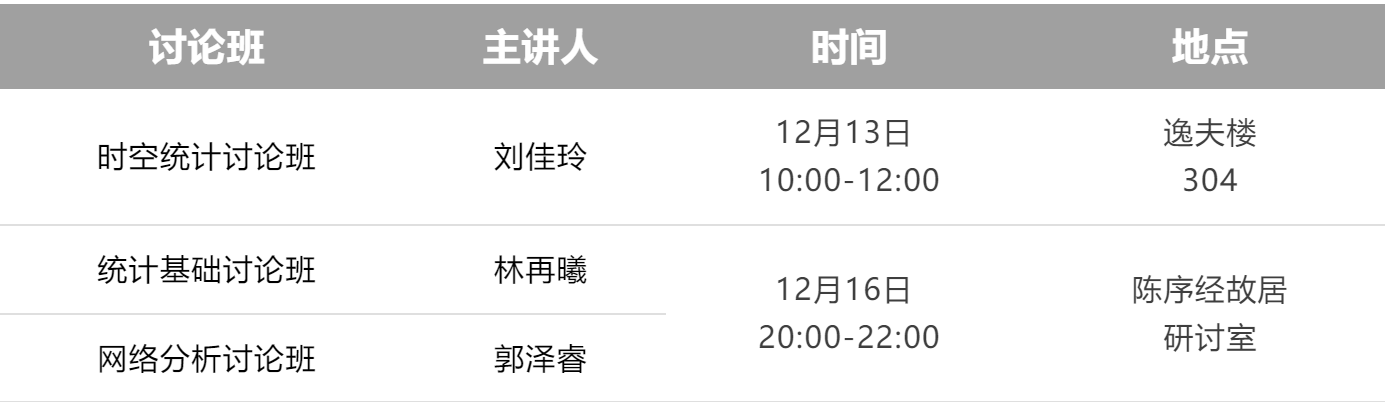
2、时间及地点
3、本期内容概述
时空统计讨论班
Spatiotemporal GAMs
We will look into spatiotemporal GAMs in this seminar.
In the analysis of spatiotemporal data, we frequently seek more flexible models to respond to the nonlinear patterns of the mean function. A successful way to solve this problem is to use GAMs. In general, GAM models involve a change of the mean response to having an additive form, with the additive components being smooth covariate functions (e.g., splines). Usually, the functions themselves are expressed as basis-function expansions.
统计基础讨论班
贝叶斯模型
在统计模型中,如果我们有关于模型未知参数的信息(先验),并且该信息可以被表达成概率密度的形式,则可以基于贝叶斯定理的理论框架进行推断。由此发展而来的贝叶斯学派与传统频率学派的核心矛盾是:前者将未知参数视为一个随机变量,而后者将其视为非随机的常数。
本节讨论班,我们将介绍贝叶斯定理的多种形式及用途。后续,我们还将解释先验密度的含义并结合例子进行构造演示。
网络分析讨论班
Neighborhood Reconstruction Methods
The central problem in machine learning on graphs is finding a way to incorporate information about graph structure into a machine learning model. Meanwhile, the challenge is that there is no straightforward way to encode this high-dimensional, non-Euclidean information about graph structure into a feature vector. We will focus on some representation learning approaches that embed nodes as points in a low-dimensional vector space. The goal is to optimize this mapping so that geometric relationships in the embedding space reflect the structure of the original graph. After optimizing the embedding space, the learned embeddings can be used as feature input for downstream machine learning tasks.


